Audio editor online? Yeah, it’s way more than just slapping some effects on a track. We’re talking a whole evolution here, from clunky desktop software to sleek, accessible online tools that are changing how everyone, from podcasters to bedroom producers, crafts audio. This deep dive explores the current landscape of online audio editors, examining their features, user experience, and the future of this rapidly expanding field.
We’ll cover everything from comparing the top players like Audacity (online) and others, to exploring the nitty-gritty details of file formats, integration with other apps, and even the security and privacy implications of using these online services. Think of it as your ultimate guide to navigating the world of online audio editing – no prior experience necessary!
Popularity and Trends of Online Audio Editors
Online audio editing has exploded in popularity over the past decade, transforming from a niche hobbyist activity to a widely accessible tool for professionals and amateurs alike. This surge is driven by several factors, including increased internet speeds, the proliferation of affordable microphones and recording devices, and the development of increasingly sophisticated yet user-friendly online platforms. The ease of access and collaborative features offered by these tools have significantly impacted the audio production landscape.The evolution of online audio editing tools has been remarkable.
Initially, these platforms were often limited in functionality, offering basic editing capabilities like trimming and joining audio files. However, recent advancements have seen the integration of advanced features like noise reduction, equalization, compression, and even mastering tools, blurring the lines between online and desktop software. This evolution has been fueled by competition and the constant demand for more powerful and versatile tools accessible directly through a web browser.
Market Share of Top Online Audio Editors
Determining precise market share for online audio editors is challenging due to the lack of publicly available, comprehensive data. However, based on user reviews, website traffic, and industry observation, we can identify several leading contenders. Audacity, a free and open-source option, maintains a significant user base due to its extensive features and community support. Other popular choices include online platforms offered by companies such as Adobe (Audition), which often leverage existing user bases and subscription models, and smaller, specialized tools focusing on specific niches like podcasting or music creation.
These platforms frequently incorporate features that streamline workflows for their target audiences, influencing market penetration. Precise numerical breakdowns are difficult to obtain, but these platforms represent the most prominent players in the current landscape.
Key Features Driving User Adoption
Several key features have propelled the widespread adoption of online audio editors. The most significant is undoubtedly accessibility. Unlike desktop software, online editors require no download or installation, making them instantly available on any device with an internet connection. This eliminates software compatibility issues and simplifies the onboarding process for new users. Another crucial factor is collaboration features; many platforms offer real-time collaborative editing, allowing multiple users to work on a project simultaneously.
This is particularly valuable for team-based projects or remote collaborations. Furthermore, the integration of AI-powered features like automatic noise reduction and transcription is also increasing user adoption, streamlining workflows and making professional-level editing more accessible to a wider audience.
Types of Users Benefiting from Online Audio Editing Software
Online audio editing software caters to a diverse range of users. Podcasters frequently utilize these platforms for editing and mastering their episodes, leveraging features like noise reduction and music insertion. Musicians use online editors for quick edits, mixing, and mastering, especially for smaller projects or collaborations. Educators and students use them for creating audio lectures, podcasts, and presentations, benefitting from the ease of use and accessibility.
Finally, even everyday users may employ these tools for simple tasks like trimming audio clips for social media or creating personalized ringtones. The versatility of these tools makes them beneficial across a broad spectrum of applications.
Feature Comparison of Leading Online Audio Editors
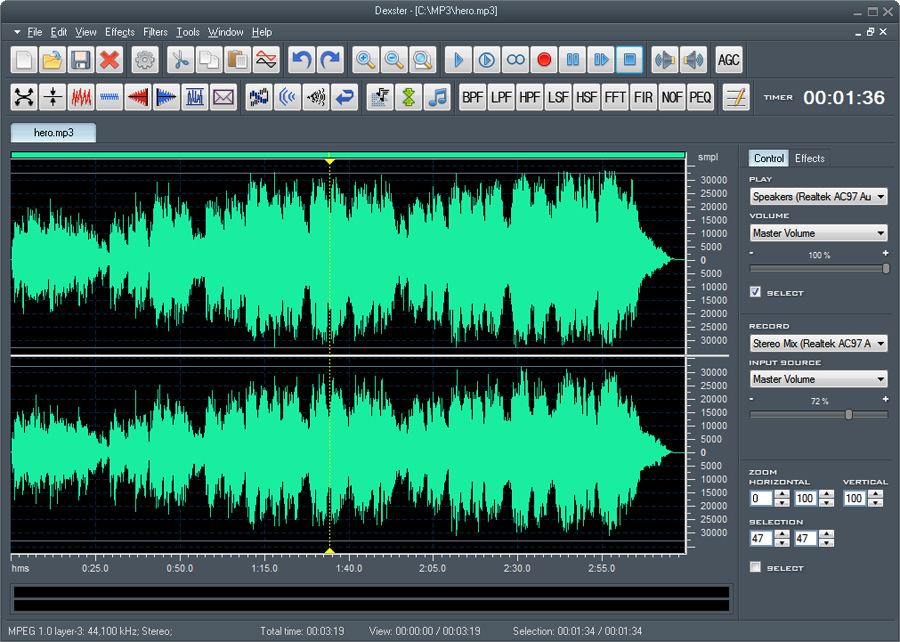
Choosing the right online audio editor can feel like navigating a minefield of features and pricing models. This section dives into a comparison of four popular options, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses to help you find the perfect fit for your audio editing needs. We’ll look at Audacity (online version), along with three other leading contenders, examining their capabilities and user-friendliness.
Audacity Online, Descript, Adobe Audition (Online), and TwistedWave: A Feature Comparison
The online audio editing landscape is diverse, with each platform offering a unique blend of features and pricing. This table summarizes the key differences between Audacity (online), Descript, Adobe Audition (online), and TwistedWave.
| Feature | Audacity Online | Descript | Adobe Audition (Online) | TwistedWave |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Free | Paid (subscription based) | Paid (subscription based, part of Adobe Creative Cloud) | Paid (per-project or subscription) |
| Basic Editing Tools (Cut, Copy, Paste, etc.) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Advanced Effects (EQ, Compression, Reverb) | Limited, mostly requires plugins | Yes, robust selection | Extensive, professional-grade | Good selection, easy to use |
| Noise Reduction | Yes | Yes | Yes, advanced algorithms | Yes |
| Transcription Capabilities | No | Yes, a key feature | No | No |
| Collaboration Tools | No | Yes | Limited, mainly through cloud storage integration | No |
| Multitrack Editing | Limited | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Ease of Use Comparison
Ease of use is subjective, but generally, Audacity Online, while powerful, has a steeper learning curve due to its less intuitive interface compared to other options. Its reliance on plugins for many advanced effects can also be a barrier for new users. Descript, on the other hand, prioritizes user-friendliness with a more streamlined interface and intuitive workflow, particularly for its transcription and collaboration features.
Adobe Audition (online) offers a professional-grade experience but requires a higher level of audio editing knowledge. TwistedWave strikes a balance between power and simplicity, making it a good choice for users who want more advanced features without the complexity of Audition.
Ideal Online Audio Editor User Interface Flowchart
An ideal online audio editor should prioritize a clear and intuitive workflow. The flowchart below illustrates a simplified user experience focusing on key tasks.[Imagine a flowchart here. It would start with “Open Project,” branching to “Import Audio” and “Create New Project.” From “Import Audio,” it would lead to “Edit Audio” (with sub-branches for cutting, pasting, effects, etc.), and then to “Export Audio.” From “Create New Project,” it would go directly to “Edit Audio.” All paths would eventually converge at “Save Project.”] The goal is to make the core editing functions readily accessible, with advanced features easily discoverable through a well-organized menu system.
The interface should be visually clean and uncluttered, using clear icons and labels to guide the user. This design emphasizes efficiency and ease of use, particularly for users with varying levels of audio editing experience.
User Experience and Interface Design
A killer user interface (UI) is the secret sauce for any successful online audio editor. No matter how powerful the underlying technology is, a clunky or confusing interface will drive users away faster than a bad reverb effect. Intuitive design is paramount, ensuring even beginners can quickly grasp the basics and start creating. The goal is seamless workflow, allowing users to focus on their audio, not the software.Intuitive user interfaces in online audio editing software are crucial for broad adoption and user satisfaction.
A well-designed interface minimizes the learning curve, allowing users of all skill levels to quickly become productive. Poor design, conversely, leads to frustration, abandonment, and negative reviews. This directly impacts the software’s market share and overall success. Consider the difference between a software with clearly labeled buttons and a logical layout versus one with cryptic icons and a confusing workflow.
The former fosters engagement, while the latter breeds frustration.
Effective Visual Cues and Feedback Mechanisms
Effective visual cues and feedback are essential for guiding users through the editing process. Visual indicators such as waveform highlighting during selection, real-time effects previews, and clear visual representations of audio levels provide immediate feedback, allowing users to understand the consequences of their actions without delay. For instance, a clear visual representation of the volume levels across different frequency bands (using a spectrum analyzer) is far more informative than just a single master volume meter.
Similarly, using color-coding to differentiate between different audio tracks or effects can significantly improve clarity and reduce cognitive load. A simple example would be using different colors for vocal tracks, instrument tracks, and effects tracks, making it easy to identify and manage them.
Best Practices for Designing User-Friendly Online Audio Editors
A user-friendly online audio editor prioritizes simplicity and efficiency. Here are some key design principles:
- Clear and Concise Labeling: All buttons, tools, and menus should be clearly labeled with easily understandable terms.
- Logical Layout: Tools and features should be organized logically, grouping related functions together. A common approach is to use a sidebar for tools and a main workspace for the audio waveform.
- Intuitive Shortcuts: Keyboard shortcuts should be implemented for common actions, speeding up the workflow for experienced users.
- Visual Feedback: Real-time visual feedback should be provided for all actions, so users immediately see the effects of their edits.
- Undo/Redo Functionality: A robust undo/redo system is crucial for allowing users to experiment without fear of irreversible mistakes.
- Responsive Design: The interface should adapt seamlessly to different screen sizes and devices.
- Accessibility Features: Consider users with disabilities and incorporate features like keyboard navigation and screen reader compatibility.
Impact of Color Palettes and Typography
The choice of color palette and typography significantly influences the user experience. A well-chosen color palette enhances readability and creates a visually appealing interface. For example, using a dark background with light text can reduce eye strain during long editing sessions. Typography plays a crucial role in readability. Clear, legible fonts should be used for all text elements, ensuring ease of reading, even for small text sizes.
Avoid overly decorative or difficult-to-read fonts. Audacity, for instance, utilizes a clean, functional font that prioritizes readability over stylistic flair, which contributes to its user-friendly nature. Conversely, using clashing colors or illegible fonts can lead to a frustrating and unproductive editing experience. The overall aesthetic should be clean, modern, and uncluttered, allowing the user to focus on the audio itself.
Audio File Formats and Compatibility: Audio Editor Online
Online audio editors offer a convenient way to manipulate audio, but their capabilities are often tied to the file formats they support. Understanding these limitations is crucial for choosing the right editor and managing your audio projects effectively. Different formats impact file size, audio quality, and the overall editing experience.
The compatibility of online audio editors with various audio file formats varies significantly. Most commonly support MP3, WAV, and sometimes AAC, but support for less common formats like FLAC or Ogg Vorbis is less widespread. This is largely due to the complexities of handling different codecs within a browser-based environment. The limitations become more apparent when dealing with large files or high-resolution audio, which can strain the browser’s resources and lead to performance issues, such as lag or crashes.
Supported Audio File Formats
The choice of audio codec directly influences both the file size and the audio quality. MP3, for example, uses lossy compression, resulting in smaller file sizes but some loss of audio information. WAV, on the other hand, is an uncompressed format, preserving all audio data but resulting in much larger file sizes. AAC offers a balance between file size and quality, making it a popular choice for online streaming.
These trade-offs become particularly relevant when working with online editors, where upload and download speeds and browser processing power are limiting factors.
Limitations of Online Editors with Large or High-Resolution Files
Online audio editors typically have limitations on the size of files they can handle. Uploading and processing large, high-resolution audio files (e.g., 24-bit/96kHz WAV files) can be slow, prone to errors, or even impossible depending on the editor and your internet connection. The browser’s processing power is a major constraint; complex operations on large files may lead to significant lag, freezing, or even crashes.
This contrasts sharply with desktop audio editing software, which can handle much larger and higher-resolution files with greater ease.
Implications of Audio Codecs on File Size and Quality
The choice of audio codec directly impacts both file size and audio quality. Lossy codecs like MP3 and AAC reduce file size by discarding some audio data deemed less important to human hearing. This results in smaller files, beneficial for online sharing and storage, but at the cost of some audio fidelity. Lossless codecs like WAV and FLAC preserve all audio data, leading to larger files but maintaining the original audio quality.
For online editing, the balance between file size and quality is a key consideration, as larger files require more processing power and upload/download time.
Comparison of Supported File Formats, Audio editor online
| Online Audio Editor | MP3 | WAV | AAC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Audacity (online version) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| TwistedWave | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Soundtrap | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Adobe Audition (online version – limited features) | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
(Note: Support may vary depending on the specific version and features of the online editor. Always check the editor’s documentation for the most up-to-date information.)
Integration with Other Software and Services
Online audio editors are increasingly becoming more than just standalone applications; they’re integrating seamlessly with other software and services, enhancing workflow and boosting creative possibilities. This interconnectedness is crucial for modern audio production, allowing for a more fluid and efficient process. This section will explore how these integrations work, their benefits, and some examples of successful implementations.The ability to seamlessly integrate with other applications is a key differentiator for online audio editors.
This integration enhances productivity and creative potential by streamlining workflows and expanding possibilities beyond the editor’s core functionality. Different integration types offer distinct advantages and challenges, which we’ll delve into below.
Cloud Storage Integration
Many online audio editors boast native integration with popular cloud storage services like Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive. This allows users to directly import audio files from their cloud storage accounts, eliminating the need for manual downloads and uploads. Similarly, edited projects can be saved directly back to the cloud, providing automatic backups and easy access from multiple devices.
This streamlined workflow drastically reduces the time spent managing files and improves overall efficiency. For example, a user working on a podcast could directly import audio clips from their Google Drive folder, edit them within the online editor, and then save the final product back to their cloud storage, ready for distribution.
Integration with Video Editing Software
The integration of online audio editors with video editing software represents a significant step towards a more unified creative workflow. Imagine a scenario where you can directly export audio from your online editor to a video editing platform like Adobe Premiere Pro or DaVinci Resolve, without needing to manually handle file transfers. This seamless transition allows for synchronized audio and video editing, simplifying post-production and improving the overall quality of the final product.
While full integration is still developing in many cases, the ability to easily import and export audio files in common formats (like WAV or MP3) between these platforms is already a major advantage.
Collaborative Platforms Integration
The potential for integration with collaborative platforms like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365 is immense. This allows multiple users to work on the same audio project simultaneously, fostering teamwork and streamlining collaborative audio production. However, challenges include managing simultaneous edits, ensuring version control, and addressing potential conflicts. Successful implementations often involve real-time collaboration features, allowing users to see each other’s edits and communicate within the editor itself.
Imagine a team of musicians collaborating on a song, each editing their respective tracks simultaneously within the online audio editor, communicating through an integrated chat function. This real-time collaboration feature significantly accelerates the creative process.
Examples of Successful Integrations
Several online audio editors showcase successful integrations. For instance, some editors directly integrate with social media platforms, allowing users to easily share their finished projects. Others offer plugins or APIs that allow for deeper integration with other applications, expanding their functionality. These integrations demonstrate the evolving landscape of online audio editing and its increasing interconnectedness with other creative tools and platforms.
The success of these integrations depends heavily on user-friendliness, robust functionality, and seamless data transfer.
Security and Privacy Considerations

Using online audio editors offers convenience, but it’s crucial to understand the security and privacy implications. These services handle sensitive audio data, raising concerns about potential breaches and misuse. This section examines the security measures employed by various platforms and explores strategies for protecting your privacy.
Data Encryption and Storage
Online audio editors typically employ various security measures to protect user data. Many utilize HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) to encrypt data transmitted between the user’s browser and the editor’s servers. This prevents eavesdropping on your audio files during upload and download. Furthermore, reputable services often encrypt data at rest, meaning your files are secured even when stored on their servers.
The specific encryption methods vary between providers, with some using AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) with strong key lengths. However, it’s essential to check the specific security practices Artikeld in each service’s privacy policy for a complete picture. For instance, some services might use different encryption for data in transit versus data at rest.
Privacy Risks Associated with Online Audio Editors
Using online audio editing services introduces potential privacy risks. The primary concern revolves around the handling and storage of your audio files. Even with encryption, there’s a risk of data breaches due to vulnerabilities in the service’s infrastructure or malicious attacks. Additionally, the provider’s privacy policy dictates how your data is used, including potential sharing with third parties for analytics or advertising purposes.
Some services may also retain your audio files for a certain period, even after you delete them from your account. It’s vital to thoroughly review the privacy policy before using any online audio editor to understand how your data will be managed.
Data Handling and Storage Practices
The way user data is handled and stored varies significantly among online audio editors. Some services explicitly state that they don’t retain user audio files after a project is completed or deleted, focusing on a temporary storage approach. Others may store data indefinitely, citing reasons like backup or legal compliance. The location of data storage is also relevant, with some providers specifying the country or region where their servers are located.
This information influences the applicability of different data protection laws and regulations. Transparency regarding data retention policies and storage locations is crucial for informed decision-making. For example, a service might store user data in a region with stricter data protection laws compared to another service that stores data in a region with less stringent regulations.
Best Practices for Protecting Privacy
Protecting your privacy when using online audio editors requires proactive measures.
- Review the Privacy Policy: Carefully read the privacy policy of any online audio editor before using it. Pay close attention to sections on data collection, usage, sharing, and retention practices.
- Use Strong Passwords: Employ strong, unique passwords for your online audio editor accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): If available, enable 2FA for an extra layer of security.
- Limit Data Upload: Avoid uploading highly sensitive or confidential audio files unless absolutely necessary.
- Delete Files After Use: Delete your audio files from the online editor’s servers once you’ve finished working on them.
- Choose Reputable Services: Opt for well-established online audio editors with a strong reputation for security and privacy.
Pricing Models and Monetization Strategies
Online audio editors employ diverse pricing models to balance user accessibility with sustainable business practices. Understanding these models and the associated monetization strategies is crucial for both users seeking the right tool and developers aiming to build a successful platform. This section will explore the common pricing models, their pros and cons, and various monetization techniques used in the online audio editing industry.
Pricing Model Comparison
Three main pricing models dominate the online audio editor market: freemium, subscription, and one-time purchase. Each offers a different value proposition to both the user and the provider. The optimal choice depends heavily on the target audience and the complexity of the software offered.
Freemium Model Advantages and Disadvantages
The freemium model offers a basic version of the software for free, while premium features are available through a paid subscription or one-time purchase. For users, this provides a low-risk entry point to explore the software’s capabilities. However, the free version often has limitations, such as watermarks on exported audio, restricted file sizes, or a limited number of effects.
For providers, this model attracts a large user base, but converting free users to paying customers can be challenging. Revenue is heavily dependent on the conversion rate.
Subscription Model Advantages and Disadvantages
Subscription models involve recurring payments for access to the software’s full features. Users benefit from consistent access to updates and new features. However, the recurring cost can be a barrier for some users, and cancellations might lead to feature loss. For providers, subscription models provide a predictable revenue stream and encourage user retention. It’s easier to implement feature updates as users are already paying for access.
One-Time Purchase Model Advantages and Disadvantages
In a one-time purchase model, users pay a single upfront fee for lifetime access to the software. This offers users a clear cost and avoids recurring payments. However, users don’t receive automatic updates or new features unless they purchase a new version. For providers, this model offers a large initial revenue surge, but there’s no recurring income and maintaining the software can be costly in the long run.
Monetization Strategies
Beyond the core pricing models, online audio editor companies employ several monetization strategies to generate revenue. These include advertising (on free tiers), premium features (within freemium models), in-app purchases (for additional effects or sound libraries), and affiliate marketing (partnering with related services).
Pricing and Feature Comparison Table
| Service Name | Pricing Model | Basic Features | Premium Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Audacity (Online) | Freemium (Donations encouraged) | Basic editing, recording, effects | Advanced effects, VST plugin support (often requires desktop version) |
| Soundtrap | Subscription | Collaboration tools, basic effects | Advanced effects, larger project storage |
| TwistedWave | One-time purchase & Subscription | Basic editing, effects | Advanced features, higher resolution audio support (subscription) |
| Adobe Audition (Cloud) | Subscription (part of Adobe Creative Cloud) | Comprehensive editing, effects, restoration tools | Access to full Adobe Creative Cloud suite |
Accessibility Features and Inclusivity
Online audio editors, while offering powerful tools for sound manipulation, often fall short in providing truly inclusive experiences for users with disabilities. Accessibility isn’t just a matter of compliance; it’s about ensuring everyone can participate in the creative process. This section explores the current state of accessibility in online audio editors, identifies areas for improvement, and offers recommendations for a more inclusive future.
Keyboard Navigation and Screen Reader Compatibility
Many online audio editors rely heavily on mouse interactions. This presents significant barriers for users who rely on keyboard navigation or screen readers. Effective keyboard navigation requires logical tab order, clear labels for interactive elements, and the ability to control all editor functions using only the keyboard. Screen reader compatibility necessitates detailed alternative text descriptions for all visual elements, including waveforms, controls, and interface components.
Some editors are better than others in this regard; for example, Audacity (while not strictly online) offers excellent keyboard shortcuts and screen reader support, setting a high benchmark. However, many online options lag behind, leaving blind or visually impaired users struggling to navigate the interface effectively.
Color Contrast and Visual Clarity
Poor color contrast can render interfaces unusable for users with low vision. Adequate color contrast between text and background, and between different interactive elements, is crucial for readability. Similarly, visual clarity involves using appropriately sized fonts, sufficient spacing between elements, and avoiding cluttered layouts. Online audio editors should adhere to WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) recommendations for color contrast ratios and ensure that all visual information is presented in a clear and understandable way.
For example, a waveform display should have adjustable contrast and thickness to suit individual needs.
Captioning and Transcription Support
For users who are deaf or hard of hearing, the ability to add captions or transcriptions to audio projects is paramount. While not a core feature of all online editors, this functionality would dramatically improve inclusivity. Ideally, the editor would integrate with automated transcription services or allow users to upload their own captions in standard formats like SRT.
Moreover, the interface should allow users to easily adjust the size and style of captions. The absence of such features currently limits the accessibility of online audio editing for a significant portion of the population.
Customizable Interface Elements
Providing customizable interface elements, such as font size, color schemes, and layout options, empowers users to tailor the editor to their specific needs and preferences. This is especially important for users with visual impairments or cognitive disabilities. Offering a dark mode, for example, can reduce eye strain and improve usability for many. Allowing users to increase the size of buttons and other interactive elements makes the interface more accessible for those with motor impairments or limited dexterity.
Recommendations for Improving Accessibility
Implementing robust accessibility features requires a multifaceted approach. Here’s a list of key recommendations:
- Adhere strictly to WCAG guidelines.
- Conduct thorough accessibility audits with users with disabilities.
- Invest in automated accessibility testing tools.
- Provide comprehensive keyboard navigation and screen reader support.
- Offer customizable interface elements, including font size, color schemes, and layout options.
- Integrate with captioning and transcription services.
- Offer alternative input methods, such as voice control.
The Future of Online Audio Editing
Online audio editing is poised for a significant transformation, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, web technologies, and evolving user needs. We’re moving beyond simple waveform manipulation towards a future where intelligent tools empower creators of all skill levels to produce professional-quality audio with unprecedented ease and efficiency.The convergence of several key technological trends will shape the future of online audio editing.
These advancements promise to make the process faster, more intuitive, and accessible to a broader audience.
AI-Powered Features in Online Audio Editing
AI is rapidly changing the landscape of audio editing. We can expect to see a surge in AI-powered features that automate time-consuming tasks, enhance audio quality, and provide creative assistance. For instance, imagine an online editor that automatically removes background noise with far greater precision than current methods, or one that intelligently identifies and separates different audio sources within a complex mix.
AI-driven transcription and translation capabilities are also on the horizon, opening up new possibilities for accessibility and international collaboration. Furthermore, AI could generate unique sound effects or musical elements based on user input, dramatically expanding creative possibilities for less technically proficient users. Think of it as having a virtual sound engineer and composer built right into your browser.
Okay, so you’re looking for a killer online audio editor, right? Finding the perfect tool can be a total drag, but think about it this way: just like you need precise vector editing in coreldraw for graphics, you need equally precise tools for audio. A good audio editor online lets you fine-tune everything, giving you the same level of control over sound that CorelDRAW gives you over images.
Impact of WebAssembly on Performance
WebAssembly (Wasm) is a binary instruction format designed for fast execution in web browsers. Its adoption will significantly improve the performance of online audio editing tools. Currently, many online editors struggle with real-time processing of large audio files. Wasm allows for near-native performance of complex audio algorithms within the browser, eliminating the latency and limitations associated with JavaScript-based processing.
This means smoother editing experiences, even with high-resolution audio files and computationally intensive effects. This improved performance is crucial for professional users who require precise control and real-time feedback. For example, a Wasm-powered online editor could handle multi-track editing of high-resolution audio without noticeable lag, a significant improvement over current limitations.
Future Trends in the Online Audio Editing Market
The online audio editing market is expected to witness increasing competition and innovation. We predict a rise in specialized online editors catering to niche markets, such as podcasting, voice-over work, and music production. Subscription models with tiered access to advanced features and AI-powered tools will become increasingly prevalent. Moreover, the integration of online audio editors with other creative tools and platforms will become seamless, fostering a more collaborative and integrated workflow for content creators.
The success of platforms like Canva in the graphic design space suggests a similar trajectory for online audio editing, with user-friendly interfaces and powerful features driving adoption.
Evolution of Online Audio Editor Interfaces and Functionalities
Future online audio editors will likely feature more intuitive and visually engaging interfaces. We anticipate the adoption of advanced visualization techniques to help users understand complex audio signals more easily. Gesture-based controls and AI-powered suggestions will streamline workflows and empower users with less technical expertise. The integration of collaborative editing features, allowing multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously, will also become more common.
Consider an interface that uses AI to suggest edits based on the style and context of the audio, or one that automatically aligns multiple audio tracks based on their content. These features will dramatically improve the efficiency and ease of use for both novice and experienced users.
Case Studies of Successful Online Audio Editors
The success of online audio editors hinges on a combination of factors, including intuitive user interfaces, powerful features, effective marketing, and a strong understanding of their target audience. Analyzing successful platforms reveals key strategies and provides valuable insights for future development in the field. This section will delve into the success stories of several prominent online audio editors, examining their unique approaches and contributions to the market.
Audacity’s Open-Source Dominance
Audacity, a free, open-source, cross-platform digital audio editor and recorder, stands as a testament to the power of community and accessibility. Its success stems from its robust feature set, catering to both beginners and experienced users. Audacity offers a wide range of functionalities including recording, editing, mixing, mastering, and effects processing. Its open-source nature fosters a large and active community of developers and users, constantly contributing to its improvement and expansion.
This collaborative environment ensures continuous updates, bug fixes, and the addition of new features based on user feedback. Audacity’s marketing strategy relies heavily on word-of-mouth and organic growth within online communities focused on audio production and digital media. Its free availability significantly lowers the barrier to entry, attracting a broad user base across various skill levels and geographic locations.
Descript’s AI-Powered Approach
Descript, a subscription-based audio and video editor, has carved a niche for itself by integrating powerful AI capabilities into its platform. Descript’s AI-powered transcription and editing features streamline the workflow for podcasters, filmmakers, and other content creators. The ability to edit audio by simply editing the text transcription is a revolutionary feature that significantly increases efficiency. Descript’s success is attributable to its innovative use of technology, targeted marketing towards professional users, and a strong emphasis on user experience.
Their marketing focuses on showcasing the time-saving benefits of their AI features and targets professionals who value efficiency and high-quality output. The subscription model allows for continuous investment in research and development, ensuring the platform remains at the forefront of audio editing technology.
Adobe Audition’s Industry Standard Status
Adobe Audition, a professional-grade audio workstation integrated within the Adobe Creative Cloud suite, benefits from the established brand recognition and extensive user base of the Adobe ecosystem. Its powerful features, including advanced noise reduction, restoration tools, and multitrack editing capabilities, make it a favorite among audio professionals. Adobe’s extensive marketing efforts, leveraging its existing brand and strong distribution network, have been instrumental in establishing Audition as an industry standard.
Its integration with other Adobe products, such as Premiere Pro and After Effects, provides a seamless workflow for video and multimedia projects. The subscription-based model ensures consistent revenue streams, enabling Adobe to continually invest in improving and expanding Audition’s functionalities.
Comparative Analysis of Success Factors
| Online Audio Editor | Key Success Factor 1 | Key Success Factor 2 | Key Success Factor 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Audacity | Open-source, community-driven development | Free accessibility and broad user base | Robust feature set catering to diverse skill levels |
| Descript | Innovative AI-powered features | Targeted marketing towards professional users | Focus on user experience and efficiency |
| Adobe Audition | Integration within the Adobe Creative Cloud ecosystem | Strong brand recognition and established user base | Powerful professional-grade features |
Closing Notes
So, there you have it – a comprehensive look at the exciting world of online audio editors. From their humble beginnings to their current dominance in audio production, these tools have democratized audio editing, making it accessible to everyone. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more powerful and user-friendly online audio editors to emerge, further blurring the lines between professional and amateur audio creation.
Get out there and start experimenting!
FAQ Compilation
What’s the best online audio editor for beginners?
That really depends on your needs, but many find tools with intuitive interfaces and simple editing features best for starting out. Look for editors with good tutorials and support.
Are online audio editors safe for my files?
Reputable online audio editors employ security measures to protect user data, but it’s always wise to check their privacy policies and choose well-established services. Avoid uploading highly sensitive material.
Can I use online audio editors for professional work?
Absolutely! Many professionals use online audio editors for various tasks, especially for quick edits or collaborative projects. The quality of results depends on the editor and your skills.
How much storage do online audio editors typically offer?
Storage varies widely depending on the service and your subscription level. Some offer limited free storage, while others provide generous amounts with paid plans. Check individual editor’s details.
What if I don’t have a strong internet connection?
Online audio editors require a stable internet connection for optimal performance. Lag or interruptions can affect your workflow. Consider using offline software if your connection is unreliable.
